Cloud Native
Cloud Native Computing Foundation
- Non-profit organization under the Linux Foundation
- supports cloud-native open-source projects
Role of CNCF
- Creating sustainable ecosystems for cloud-native software
- Improving developer experience
- Hosting influential open-source projects (e.g., Kubernetes, Prometheus, Helm, Envoy, gRPC)
Cloud Hosting Models:
IaaS - CaaS - PaaS - FaaS - SaaS - Serverless
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Virtualized computing resources (VMs, storage, networking)
- Users control infrastructure, provider manages physical hardware
- Example: Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines
CaaS (Container as a Service)
- Deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications
- Provider manages infrastructure and container orchestration
- Example: Google Kubernetes Engine, Amazon ECS, EKS, Fargate
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about infrastructure
- Provider manages infrastructure, servers, networking, OS, etc.
- Example: Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service
FaaS (Function as a Service)
- Deploy individual functions, executed in response to events/triggers
- Provider manages infrastructure and auto-scales functions
- Example: AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions
SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Software provided over the internet, eliminating need for installation
- Provider manages infrastructure, application, and data
- Example: Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365
Serverless
- Cloud provider manages infrastructure and auto-scales resources
- Pay only for resources consumed
- Example: Azure Functions with Azure Cosmos DB, AWS Lambda with Amazon DynamoDB
FaaS is a specific implementation of serverless computing
Macroservices to Nanoservices
Monolithic -> Modular Monolithic -> Microservices -> Nanoservices (Serverless Functions)
Cloud-Native Pillars
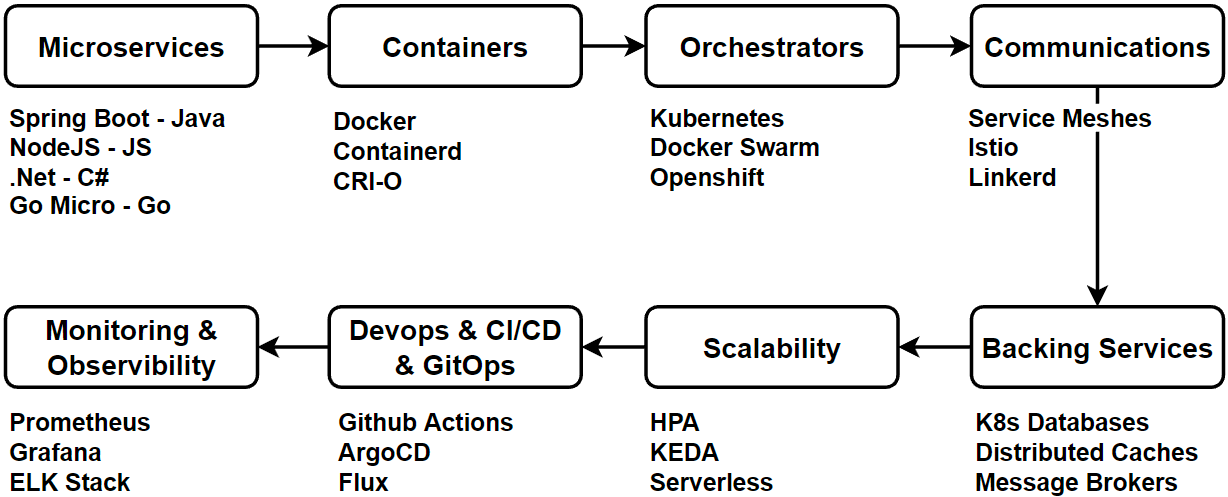
Cloud Native Architecture Design Principles
- Designed as Loosely Coupled Microservices
- Developed with Best-optimum Languages and Frameworks
- API Centric Interaction and Collaboration
- Stateless and Massively Scalable
- Elasticity and Dynamic Scaling
- Design for Resiliency
- Polyglot Architecture - Utilize the most appropriate language or technology for each component, considering team skill sets and time-to-market.
- Packaged Lightweight Containers and Orchestration
- Immutable Infrastructure - S
- Servers for hosting cloud-native applications remain unchanged after deployment. By avoiding manual upgrades, immutable infrastructure makes cloud-native deployment a predictable process