Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP)
Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) in Spring Boot is used to separate cross-cutting concerns (like logging exceptions) from the business logic of an application.
Cross-cutting concerns are aspects of a program that affect multiple modules, such as logging, security, and transaction management.
Key Concepts
Aspect:
A module that encapsulates a cross-cutting concern. It defines the code that should be executed at specific points in the application.
Join Point:
A point during the execution of the application where an aspect can be applied. Examples include method execution, object instantiation, etc.
Advice:
The action taken (method) by an aspect at a join point. There are several types of advice:
-
Before: Executes before the join point. -
After: (finally) advice - Always executed. Executes after the join point, regardless of the outcome. -
After Returning: Executes after the join point if it completes normally. -
After Throwing: Executes if the join point throws an exception. -
Around: Most powerful - Surrounds the join point, allowing you to modify its execution.
Pointcut:
An expression that specifies where advice should be applied. It defines which join points are matched by the advice.
Weaving:
The process of integrating aspects into the codebase. This can happen at various times, such as at compile-time, load-time, or runtime.
Interceptors
interceptors are components that allow you to insert behavior before, after, or around method
executions or other join points (like field access or object construction) without modifying the actual code of those methods.
- Interceptors are a type of advice in AOP.
- They are used to intercept the execution of a method or process and apply cross-cutting concerns such as:
- Logging
- Security checks
- Transaction management
- Performance monitoring
- Caching
How Interceptors Work
Interceptors are typically used in “around” advice, which means they can:
- Execute before the target method
- Optionally proceed to the target method
- Execute after the target method
This gives them full control over the method execution.
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // Proceed to the actual method
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("Execution time: " + duration + "ms");
return result;
}
Method Interceptors: Wrap method calls
Execute logic before and after a method runs.
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.MyService.doWork(..))")
public Object logMethodCall(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Before method: " + joinPoint.getSignature());
Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // Proceed to the actual method
System.out.println("After method: " + joinPoint.getSignature());
return result;
}
}
Constructor Interceptors: Wrap object creation
Intercept and wrap logic around object instantiation.
@Aspect
public class ConstructorAspect {
@Before("execution(com.example.model.User.new(..))")
public void beforeConstructor(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Creating instance of: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
}
}
Field Interceptors: Wrap field access (read/write)
Intercept reading or writing to a field.
@Aspect
public class FieldAccessAspect {
@Before("get(String com.example.model.User.name)")
public void beforeFieldRead(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Reading field: " + joinPoint.getSignature());
}
@Before("set(String com.example.model.User.name)")
public void beforeFieldWrite(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Writing to field: " + joinPoint.getSignature());
}
}
How AOP Works in Spring Boot
-
Define Aspects: Create classes annotated with
**@Aspect**that define the cross-cutting concerns. - Configure Pointcuts: Specify where and when the advice should be applied using pointcut expressions.
- Apply Advice: Use annotations to define the type of advice and associate it with the pointcuts.
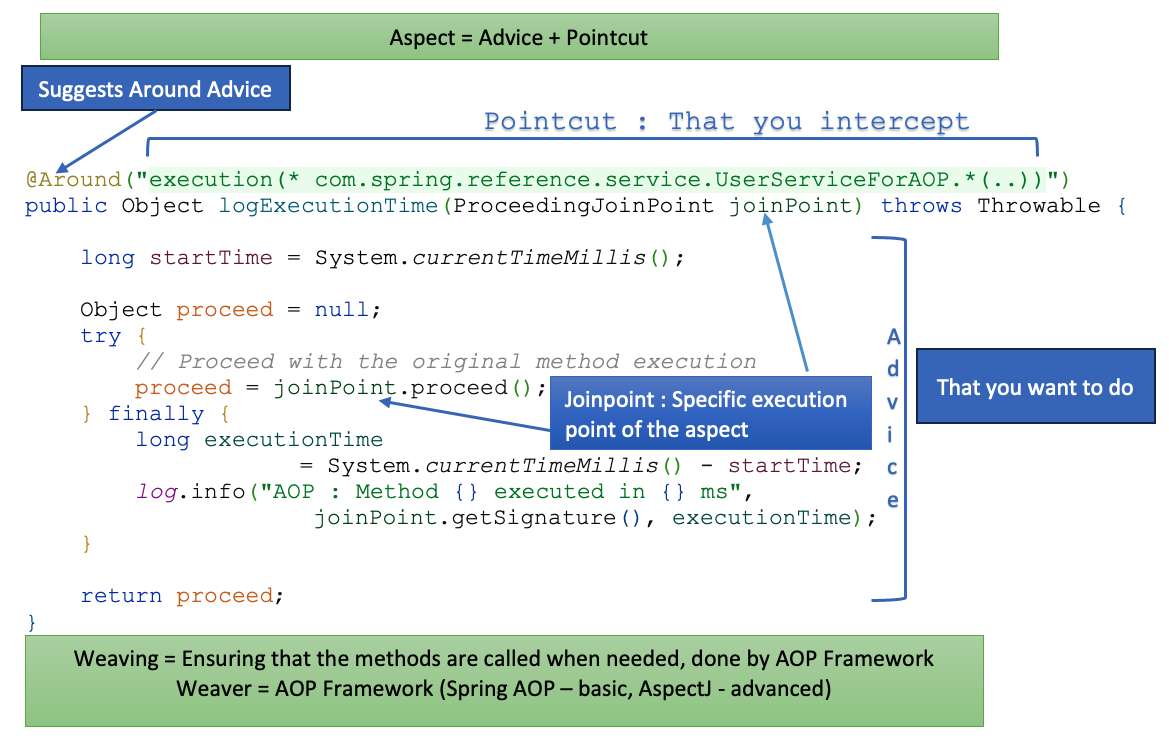
Add Dependency
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop'
Define an aspect
On Class
-
@Aspect: Marks the class as an aspect. -
@Component: Makes the aspect a Spring bean so that it can be detected by the Spring container.
On methods
-
@Before: Defines advice to execute before methods in the specified package. -
@After: Defines advice to execute after methods in the specified package. -
@Around: The most flexible type of advice because it allows you to do things like change the method’s return value, throw an exception, or completely prevent the method from running.
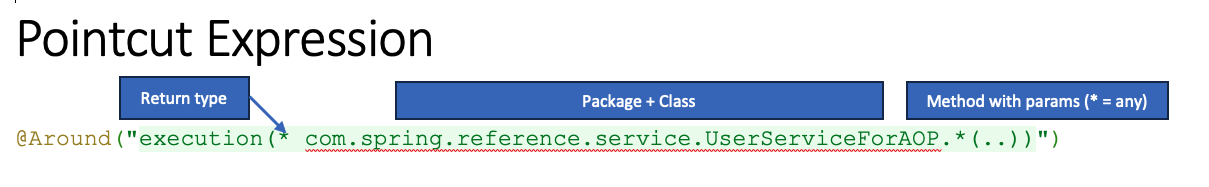
Pointcut Expression:
execution(* com.spring.reference.service.*.*(..))
- execution(…): This is a pointcut designator that specifies which method executions the advice should apply to.
-
*: Represents the return type of the method. Here, * is a wildcard that matches any return type. -
com.spring.reference.service.*.*(..):-
com.spring.reference.service: Specifies the package where the methods are located. -
*: The first * represents any class within the specified package. -
*: The second * represents any method name within the classes of the specified package. -
(..): Represents any number of parameters (including zero). The..wildcard matches any arguments.
-
Example Code
@Aspect @Component @Slf4j
public class LoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.spring.reference.service.*.*(..))")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("AOP : Before method: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
@After("execution(* com.spring.reference.service.UserServiceForAOP.*(..))") //Adding a specific Class
public void logAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("AOP : After method: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "execution(* com.spring.reference.service.UserServiceForAOP.updateUserExceptionally(..))", throwing = "exception") //Adding a specific class and its specific method
public void logAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable exception) {
log.error("AOP : Exception in method: {} with message: {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), exception.getMessage());
}
@Around("execution(* com.spring.reference.service.UserServiceForAOP.*(..))")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object proceed = null;
try {
// Proceed with the original method execution
proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
log.info("AOP : Method {} executed in {} ms", joinPoint.getSignature(), executionTime);
}
return proceed;
}
}