Kubernetes Commands
Automates
- Deployment of containers
- Scaling of containers
- Maintenance of containers
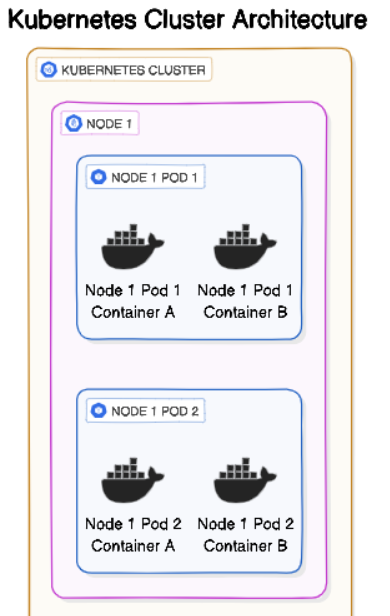
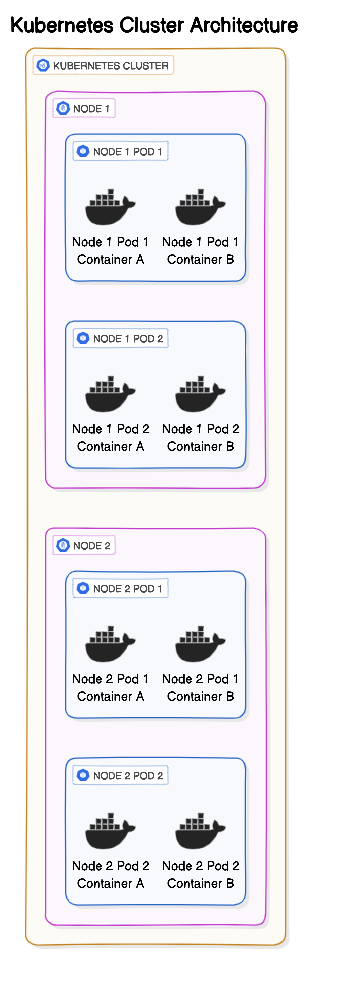
Minikube
brew install minikube
Start/shutdown the cluster
minikube start
minikube stop # Saves the state
minikube delete # Deletes everything
Dashboard
minikube dashboard
Create a namespace
kubectl create ns non-prod
Shell redirection to connect to a Pod
kubectl exec -it new-nginx -- /bin/bash
Access from Another Pod
use a temporary pod to check if the application is reachable from within the cluster
-
-i -tflag Allows us to provide input to the containerkubectl run -it --rm --restart=Never busybox --image=busybox -- sh
Then, inside the busybox shell, try to curl your application:
wget -qO- http://<your-pod-ip>:<port-number>/actuator/health
wget -qO- http://10.109.198.72:5000/actuator/health
Debugs & Checks
use autocomplete (for GCP Cloud shell)
source <(kubectl completion bash)
Pod related commands
# Get podname, status
kubectl get pods # podname from minikube dashboard can also be used
export my_pod=[your_pod_name]
#Get details like IP addres, status
kubectl describe pod $my_pod
# Services - #IpAddress, port, clusterId etc
kubectl get service nginx
Deployment related
# Deployment related
kubectl get deployments
# the rollout history of the deployment:
kubectl rollout history deployment nginx-deployment
Check Resource Usage
# to view the resource usage across the nodes of the cluster
kubectl top node
# view the resources being used by the Pod:
kubectl top pods
# Check particular pod
kubectl top pod <pod-name>
kubectl top pod todo-service-app-todo-app-7b45c8749b-ltmfw
Check Application logs
kubectl logs <pod-name>
kubectl logs todo-service-app-todo-app-7b45c8749b-ltmfw
# Running log
kubectl logs -f todo-service-app-todo-app-7b45c8749b-ltmfw
Cluster config
kubectl config view
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl config current-context
kubectl config get-contexts
# command to change the active context:
kubectl config use-context gke_${DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID}_Region_autopilot-cluster-1
source <(kubectl completion bash)
kubectl get networkpolicy
Advanced Debugging Commands
Debug Pod Issues
# Describe pod with full event history
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n ecommerce
# Get pod events sorted by timestamp
kubectl get events -n ecommerce --sort-by='.lastTimestamp'
# Check pod status with wide output (shows node, IP)
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o wide
# Get pod YAML to see full configuration
kubectl get pod <pod-name> -n ecommerce -o yaml
# Check previous container logs (if pod crashed)
kubectl logs <pod-name> -n ecommerce --previous
# Stream logs from all containers in a pod
kubectl logs <pod-name> -n ecommerce --all-containers=true -f
# Check specific container in multi-container pod
kubectl logs <pod-name> -c <container-name> -n ecommerce
Interactive Debugging
# Debug with ephemeral container (K8s 1.23+)
kubectl debug <pod-name> -n ecommerce -it --image=busybox --target=<container-name>
# Create debug pod with node's filesystem mounted
kubectl debug node/<node-name> -it --image=ubuntu
# Copy files from pod
kubectl cp <pod-name>:/path/to/file /local/path -n ecommerce
# Copy files to pod
kubectl cp /local/file <pod-name>:/path/in/pod -n ecommerce
# Execute commands in pod
kubectl exec <pod-name> -n ecommerce -- env
kubectl exec <pod-name> -n ecommerce -- ps aux
kubectl exec <pod-name> -n ecommerce -- netstat -tulpn
Network Debugging
# Test DNS resolution from pod
kubectl run -it --rm debug --image=busybox --restart=Never -- nslookup kubernetes.default
# Test service connectivity
kubectl run -it --rm debug --image=nicolaka/netshoot --restart=Never -- bash
# Then inside the pod:
# curl http://product-service.ecommerce.svc.cluster.local:8080
# nslookup product-service.ecommerce.svc.cluster.local
# traceroute product-service.ecommerce.svc.cluster.local
# Port forward to access pod directly
kubectl port-forward pod/<pod-name> 8080:8080 -n ecommerce
# Port forward to service
kubectl port-forward svc/product-service 8080:8080 -n ecommerce
# Check service endpoints
kubectl get endpoints product-service -n ecommerce
kubectl describe endpoints product-service -n ecommerce
# Test with curl pod
kubectl run curl --image=curlimages/curl -it --rm --restart=Never -- \
curl http://product-service.ecommerce.svc.cluster.local:8080/actuator/health
Resource Monitoring
# Top pods by CPU/Memory
kubectl top pods -n ecommerce --sort-by=cpu
kubectl top pods -n ecommerce --sort-by=memory
# Top nodes
kubectl top nodes --sort-by=cpu
kubectl top nodes --sort-by=memory
# Get pod resource requests and limits
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o=jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\t"}{.spec.containers[*].resources}{"\n"}{end}'
# Get all pods with their QoS class
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,QOS:.status.qosClass
# Watch pod status changes in real-time
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -w
# Get resource usage across all namespaces
kubectl top pods --all-namespaces
Persistent Volume Debugging
# List PVCs
kubectl get pvc -n ecommerce
# Describe PVC
kubectl describe pvc <pvc-name> -n ecommerce
# List PVs
kubectl get pv
# Check PV status and claims
kubectl get pv -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,STATUS:.status.phase,CLAIM:.spec.claimRef.name,STORAGECLASS:.spec.storageClassName,SIZE:.spec.capacity.storage
Multi-Container Pod Debugging
# Get logs from specific container
kubectl logs <pod-name> -c <container-name> -n ecommerce
# Exec into specific container
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -c <container-name> -n ecommerce -- /bin/sh
# Get logs from init container
kubectl logs <pod-name> -c <init-container-name> -n ecommerce
# Get logs from all containers
kubectl logs <pod-name> --all-containers=true -n ecommerce
Performance and Scaling
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA)
# Create HPA
kubectl autoscale deployment product-service --cpu-percent=70 --min=3 --max=10 -n ecommerce
# Get HPA status
kubectl get hpa -n ecommerce
# Describe HPA with detailed metrics
kubectl describe hpa product-service -n ecommerce
# Watch HPA in real-time
kubectl get hpa -n ecommerce -w
# Delete HPA
kubectl delete hpa product-service -n ecommerce
Manual Scaling
# Scale deployment
kubectl scale deployment product-service --replicas=5 -n ecommerce
# Scale statefulset
kubectl scale statefulset order-service --replicas=3 -n ecommerce
# Scale with timeout
kubectl scale deployment product-service --replicas=10 -n ecommerce --timeout=5m
# Get current replica count
kubectl get deployment product-service -n ecommerce -o=jsonpath='{.spec.replicas}'
Rollout Management
# Check rollout status
kubectl rollout status deployment/product-service -n ecommerce
# View rollout history
kubectl rollout history deployment/product-service -n ecommerce
# View specific revision
kubectl rollout history deployment/product-service --revision=2 -n ecommerce
# Rollback to previous version
kubectl rollout undo deployment/product-service -n ecommerce
# Rollback to specific revision
kubectl rollout undo deployment/product-service --to-revision=2 -n ecommerce
# Pause rollout
kubectl rollout pause deployment/product-service -n ecommerce
# Resume rollout
kubectl rollout resume deployment/product-service -n ecommerce
# Restart deployment (recreate all pods)
kubectl rollout restart deployment/product-service -n ecommerce
Security and RBAC
Check Permissions
# Check if you can perform action
kubectl auth can-i create deployments -n ecommerce
kubectl auth can-i delete pods -n ecommerce
kubectl auth can-i '*' '*' --all-namespaces
# Check permissions as different user
kubectl auth can-i get pods --as=system:serviceaccount:ecommerce:product-service-sa -n ecommerce
# List all permissions for service account
kubectl auth can-i --list --as=system:serviceaccount:ecommerce:product-service-sa -n ecommerce
Secrets Management
# Create secret from literal
kubectl create secret generic api-key --from-literal=key=my-secret-key -n ecommerce
# Create secret from file
kubectl create secret generic ssh-key --from-file=ssh-privatekey=/path/to/.ssh/id_rsa -n ecommerce
# Create TLS secret
kubectl create secret tls tls-secret --cert=/path/to/cert.crt --key=/path/to/cert.key -n ecommerce
# Get secret (base64 encoded)
kubectl get secret api-key -n ecommerce -o yaml
# Decode secret
kubectl get secret api-key -n ecommerce -o jsonpath='{.data.key}' | base64 -d
# Edit secret
kubectl edit secret api-key -n ecommerce
# Delete secret
kubectl delete secret api-key -n ecommerce
Service Accounts
# Create service account
kubectl create serviceaccount product-service-sa -n ecommerce
# Get service account token
kubectl get serviceaccount product-service-sa -n ecommerce -o yaml
# Create token for service account (K8s 1.24+)
kubectl create token product-service-sa -n ecommerce --duration=8760h
Multi-Cluster Commands
Context Management
# List all contexts
kubectl config get-contexts
# Switch context
kubectl config use-context <context-name>
# Get current context
kubectl config current-context
# Set namespace for context
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=ecommerce
# Create new context
kubectl config set-context east-cluster --cluster=east --user=east-admin --namespace=ecommerce
# Delete context
kubectl config delete-context <context-name>
Cross-Cluster Operations
# Apply to multiple clusters
for ctx in east west; do
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml --context=$ctx
done
# Get pods from all clusters
for ctx in $(kubectl config get-contexts -o name); do
echo "=== Context: $ctx ==="
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce --context=$ctx
done
# Compare resources across clusters
diff <(kubectl get pods -n ecommerce --context=east -o yaml) \
<(kubectl get pods -n ecommerce --context=west -o yaml)
Advanced Queries with JSONPath
# Get pod IPs
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.podIP}'
# Get pod names and their nodes
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\t"}{.spec.nodeName}{"\n"}{end}'
# Get all container images
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o jsonpath='{.items[*].spec.containers[*].image}' | tr -s '[[:space:]]' '\n' | sort | uniq
# Get pods with their restart count
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\t"}{.status.containerStatuses[*].restartCount}{"\n"}{end}'
# Get all pods not in Running state
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o json | jq -r '.items[] | select(.status.phase != "Running") | .metadata.name'
# Get resource requests for all pods
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce -o json | jq -r '.items[] | "\(.metadata.name): CPU=\(.spec.containers[0].resources.requests.cpu) Memory=\(.spec.containers[0].resources.requests.memory)"'
Batch Operations
# Delete all failed pods
kubectl delete pods --field-selector status.phase=Failed -n ecommerce
# Delete all completed pods
kubectl delete pods --field-selector status.phase=Succeeded -n ecommerce
# Force delete stuck pod
kubectl delete pod <pod-name> -n ecommerce --grace-period=0 --force
# Restart all pods in deployment
kubectl rollout restart deployment --all -n ecommerce
# Label all pods
kubectl label pods --all environment=production -n ecommerce
# Annotate multiple resources
kubectl annotate pods --all description="Managed by Kubernetes" -n ecommerce
Troubleshooting Scenarios
Pod in CrashLoopBackOff
# Check logs
kubectl logs <pod-name> -n ecommerce --previous
# Check events
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n ecommerce | grep -A 10 Events
# Check liveness/readiness probes
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n ecommerce | grep -A 5 "Liveness\|Readiness"
Pod Pending
# Check events for scheduling issues
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n ecommerce | grep -A 10 Events
# Check node resources
kubectl describe nodes | grep -A 5 "Allocated resources"
# Check PVC binding
kubectl get pvc -n ecommerce
Service Not Accessible
# Verify endpoints exist
kubectl get endpoints <service-name> -n ecommerce
# Check service selector matches pod labels
kubectl describe service <service-name> -n ecommerce
kubectl get pods -n ecommerce --show-labels
# Test from within cluster
kubectl run debug --image=curlimages/curl -it --rm --restart=Never -- \
curl -v http://<service-name>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local:<port>
High CPU/Memory Usage
# Identify resource-hungry pods
kubectl top pods -n ecommerce --sort-by=cpu
kubectl top pods -n ecommerce --sort-by=memory
# Check if HPA is working
kubectl get hpa -n ecommerce
kubectl describe hpa <hpa-name> -n ecommerce
# Increase resources
kubectl set resources deployment <deployment-name> -n ecommerce \
--limits=cpu=2,memory=2Gi --requests=cpu=1,memory=1Gi
Useful Aliases
Add these to your ~/.zshrc:
# Add to ~/.zshrc
alias k='kubectl'
alias kgp='kubectl get pods'
alias kgs='kubectl get svc'
alias kgd='kubectl get deployments'
alias kdp='kubectl describe pod'
alias kds='kubectl describe service'
alias kl='kubectl logs'
alias klf='kubectl logs -f'
alias kex='kubectl exec -it'
alias kctx='kubectl config use-context'
alias kns='kubectl config set-context --current --namespace'
alias kwatch='watch -n 2 kubectl get pods'
# Apply changes: source ~/.zshrc